
Children in the top 3 percent of the parental-wealth distribution also show slightly greater wealth inheritance. The fact that this is not truly the bottom of the wealth distribution explains the breakdown of the stable relationship.

This suggests not chronic, grinding poverty (the truly poor do not get to borrow much), but more likely indebtedness to finance a business venture or training.
But the parents at the bottom of the distribution have negative wealth. The greatest deviation appears in the bottom 4 percent of parental wealth, where the children are much richer than we would expect. One persistence rate, 0.20, describes inheritance across the middle 92 percent of the distribution ( Fig. Other than the top and bottom 3 or 4 percent of parental wealth, the picture has the linear character equation (23.1) assumes. The control chart will show whether there is any pattern in the error terms, and calculation of the error terms will show whether they meet the necessary conditions as a basis for computation of the confidence limits.įor example, a recent study of intergenerational wealth mobility in Sweden assembled data from Danish tax records that allows a comparison of the wealth of 1.2 million children with that of their parents ( Boserup et al., 2013) The huge size of the Danish wealth data set means that the authors can divide the parents into percentiles and look at the average wealth of children for each parent percentile, measured again as a percentile of the child wealth distribution.
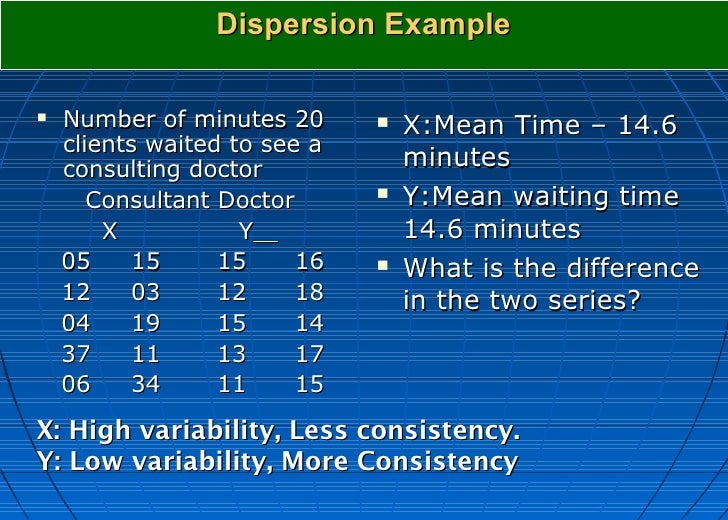
Measure of dispersio plus#
If all these conditions are met, then 68% of the outcomes will be within plus or minus one standard error, 95% will be within plus or minus twice the standard error and 99.7% will be within plus or minus three times the standard error. The errors are not serially correlated, that is, the error terms do not show a pattern, in terms of direction or size, over time. The average forecasting error is zero, that is, there is no tendency to regularly over or underestimate. A normal distribution is a model of a continuous variable whose value depends upon the effect of a number of factors, each factor exerting a small positive or negative influence. The error terms are normally distributed.

There are however some pre-requisites for the use of standard errors: 1. The standard error is particularly useful, because it can be used to compute confidence limits and, because the terms are squared, it places more emphasis on large errors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
